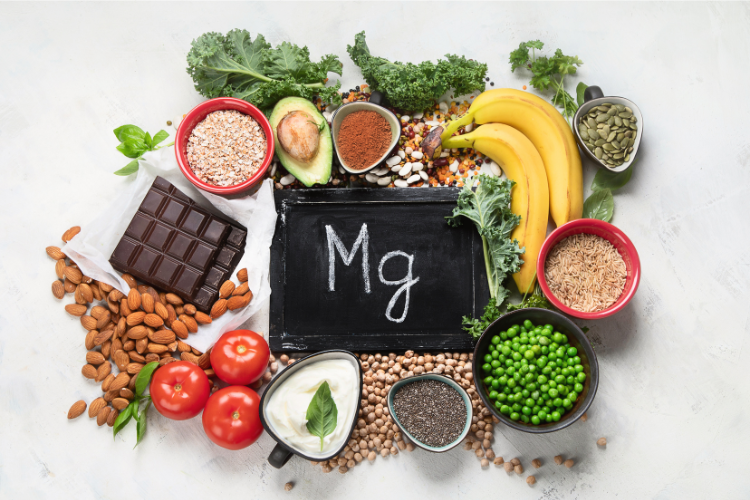Blog
8 Magnesium-Rich Foods
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in numerous physiological processes within the human body. Despite its significance, many individuals are unaware of the importance of maintaining adequate magnesium levels. In this article, we will first delve into the significance of magnesium and why it is essential for our well-being. We will then look at the prevalence of magnesium deficiency worldwide and the reasons behind this situation. We will finish by highlighting the signs, symptoms and risks associated with magnesium deficiency before to explore a variety of magnesium-rich foods.
The Importance of Magnesium
Magnesium is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body, making it crucial for various bodily functions. This mineral is responsible for maintaining proper nerve function, supporting muscle contraction and relaxation, regulating blood pressure, and promoting a healthy immune system. Magnesium also plays a vital role in bone health, energy production, and the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and proteins.

Prevalence of Magnesium Deficiency Worldwide
Magnesium deficiency is a global health concern. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 75% of adults worldwide do not meet the recommended daily intake of magnesium. In the United States alone, studies suggest that approximately 50% of the population may have insufficient magnesium levels. Similar trends have been observed in other parts of the world.
Why?
The combination of few factors contributes to the prevalence of magnesium deficiency on a global scale:
1. Inadequate Dietary Intake
Many individuals do not consume enough magnesium-rich foods in their diet. The Western diet, which is often high in processed foods, refined grains, and sugar, tends to be low in magnesium. Additionally, the consumption of convenience foods often leads to a decreased intake of nutrient-dense foods, including those rich in magnesium.
2. Soil Depletion
Modern agricultural practices have led to a decline in the mineral content of the soil. Magnesium levels in the soil directly impact the magnesium content of crops. Therefore, even if individuals consume a variety of foods, they may still not be receiving sufficient magnesium due to the depletion of minerals in the soil.
3. Increased Consumption of Processed Foods
Processed and refined foods, such as white flour, sugar, and highly processed snacks, contain minimal amounts of magnesium. These foods have become more prevalent in diets worldwide, displacing more nutrient-dense options.
4. Chronic Health Conditions
Certain health conditions can affect magnesium absorption, utilization, or excretion in the body. Conditions such as gastrointestinal disorders (Crohn’s disease, celiac disease), kidney disorders, and diabetes may increase the risk of magnesium deficiency.
5. Medications
Certain medications can interfere with magnesium absorption or increase magnesium excretion. Examples include diuretics, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and some antibiotics. Long-term use of these medications may contribute to magnesium deficiency.
6. Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can impair magnesium absorption and increase urinary excretion, leading to decreased magnesium levels in the body.
7. Increased Stress Levels
Chronic stress and anxiety can deplete magnesium levels in the body. Stress hormones released during periods of stress can affect magnesium metabolism and excretion.
Signs, Symptoms, and Risks of Magnesium Deficiency
The signs and symptoms of magnesium deficiency can vary, and they often mimic other health issues. Some common manifestations include muscle cramps, tremors, fatigue, irritability, insomnia, and irregular heartbeat.
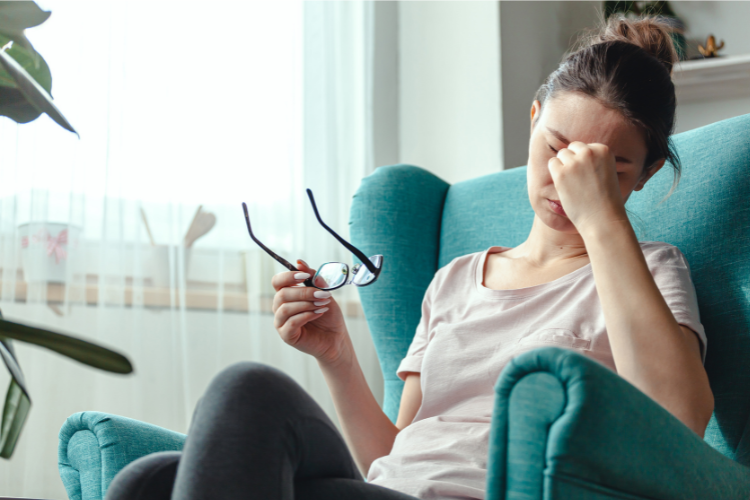

Prolonged magnesium deficiency can lead to more serious complications. It has been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, high blood pressure, osteoporosis, type 2 diabetes, and migraines. Moreover, low magnesium levels can impact mental health, contributing to symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Magnesium-Rich Foods
Maintaining a well-balanced diet that includes magnesium-rich foods is an effective way to prevent deficiency.
Here are some excellent sources of magnesium:
1. Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are rich in magnesium and other essential nutrients.
2. Avocados: This versatile fruit is not only delicious but also packed with magnesium, potassium, and healthy fats.
3. Bananas: Most well-known for their high potassium content, they’re also rich in magnesium
4. Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and halibut are not only rich in omega-3 fatty acids but also a good source of magnesium.

Fill-up on magnesium-rich organic produce at Bali Buda
We have everything in store, every day!
5. Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, cashews, pumpkin seeds, and flaxseeds are great options.
6. Legumes: Black beans, chickpeas, and lentils are not only rich in magnesium but also provide a good amount of dietary fiber.
7. Whole Grains: Quinoa, brown rice, and oats are excellent choices for increasing your magnesium intake.
8. Dark Chocolate: Indulge in a small piece of dark chocolate to satisfy your sweet tooth while benefiting from its magnesium content.
Takeaway
Magnesium is a vital mineral that is often overlooked, yet its role in maintaining optimal health cannot be understated. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet can help prevent deficiency and promote overall well-being. If you suspect magnesium deficiency, consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate testing and guidance. By prioritizing this mighty mineral, you can unlock its countless benefits and enjoy a healthier, more vibrant life.

 Indonesia
Indonesia